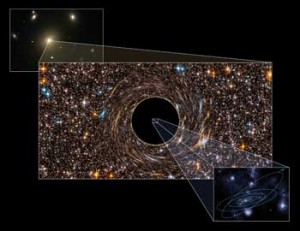
Astronomers at UC Berkeley have found the two largest black holes ever recorded, both about twice as big as the previous record holder.
Each black hole has a monster appetite, consuming everything within 1,000 light years. Their “event horizon,” the region of space from which nothing can escape, is five times the size of our solar system.
“Don’t go within 1,000 light years of these holes. You’ll never get back,” says Chung-Pei Ma, a professor of astronomy at UC Berkeley who helped make the discovery.
The black holes are each 10 billion times as massive as our own Sun. Both live at the center of galaxies, just as a black hole exists at the core of our own Milky Way galaxy. “But ours is puny by comparison,” says Ma. “It’s 2,500 times smaller than these massive black holes.”
The team used the Keck and Gemini observatories, two of the largest telescopes on Earth. “We were already pushing the limits of new technology," Ma says. "So it’s been pretty exciting to measure black holes. And we just happened to find the record breakers."